Exploring the Impact of Fluoride on the Pineal Gland: Accumulation, Calcification, and Melatonin Production
by LYL Admin, 25 Dec, 2024
Exploring the Impact of Fluoride on the Pineal Gland: Accumulation, Calcification, and Melatonin Production
Fluoride is widely known for its dental health benefits, particularly in preventing tooth decay. It is commonly found in fluoridated water and various fluoride-containing products, such as toothpaste and mouthwash. However, growing concerns have emerged about fluoride’s potential effects on the pineal gland, a small but vital endocrine organ located deep in the brain. This article explores the relationship between fluoride exposure, pineal gland calcification, and melatonin production, drawing on recent scientific research.
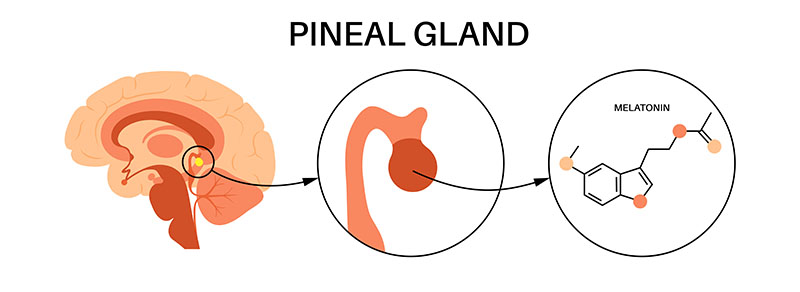
The Pineal Gland and Its Role in the Body
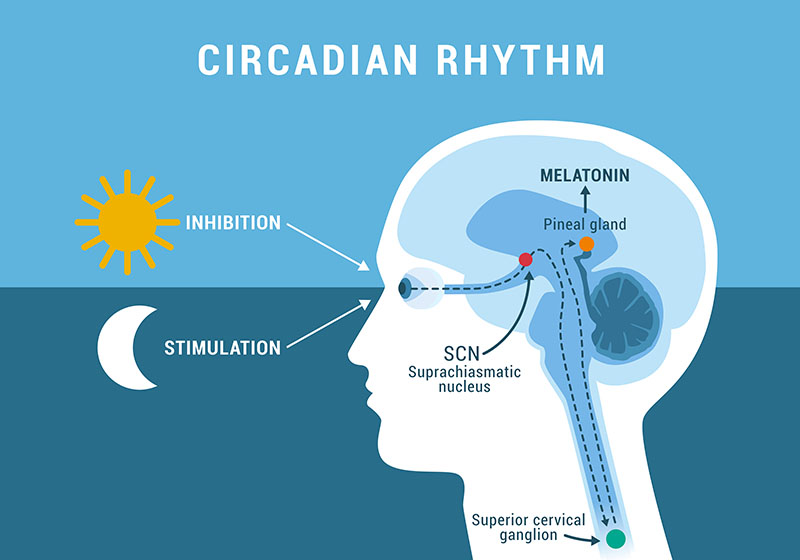
The pineal gland, often referred to as the body’s "biological clock," plays a central role in regulating circadian rhythms by producing melatonin, a hormone that influences sleep-wake cycles. Despite its small size, the gland’s functions are crucial for maintaining sleep patterns, seasonal biological rhythms, and even some aspects of aging and reproduction.
Fluoride Accumulation in the Pineal Gland
Studies have shown that the pineal gland can accumulate high levels of fluoride, primarily because it is rich in hydroxyapatite, a calcium-containing mineral that binds fluoride readily. Research published in Applied Sciences highlights that the pineal gland may become the most fluoride-saturated organ in the human body【1】.
This accumulation is associated with increased calcification of the gland, which is a natural process that can intensify with age. Excessive calcification, however, may reduce the gland’s functional capacity.
Pineal Calcification and Melatonin Production
Calcification of the pineal gland has been linked to reduced melatonin production, which can impair sleep and disrupt circadian rhythms. An article in Molecules underscores that pineal calcification may jeopardize melatonin synthesis, potentially contributing to neurological conditions【2】.
Reduced melatonin levels can have far-reaching effects, from sleep disturbances to early puberty and altered seasonal rhythms in some animals. Although the precise consequences in humans remain an active area of research, these findings raise important questions about environmental factors that may accelerate calcification, including fluoride exposure.
Fluoridated Water and Fluoride-Containing Products
The most common sources of fluoride exposure include:
- Fluoridated Water: Many municipal water supplies contain fluoride to prevent tooth decay. While deemed safe at regulated levels, concerns arise regarding cumulative exposure.
- Dental Products: Toothpaste, mouthwash, and fluoride treatments can also contribute to overall fluoride intake, particularly if inadvertently ingested.
- Dietary Sources: Certain foods and beverages, such as tea, may naturally contain fluoride.


Fluoride and Sleep Disturbances
Emerging research suggests a possible link between fluoride exposure and sleep patterns. A study in Environmental Health found that higher fluoride exposure correlated with sleep disturbances among older adolescents【3】. While more research is needed to confirm causation, this finding highlights the importance of understanding how fluoride might influence the endocrine system, particularly the pineal gland.
Practical Considerations for Reducing Fluoride Exposure
For individuals concerned about the potential effects of fluoride on the pineal gland, here are some practical steps:
- Water Filtration: Use filtration systems capable of removing fluoride, such as reverse osmosis filters.
- Moderation of Fluoride-Containing Products: Avoid overuse of dental products containing fluoride, especially for children who may swallow toothpaste.
- Awareness of Dietary Sources: Be mindful of foods and drinks that naturally contain fluoride, like tea and processed beverages.
Conclusion
The relationship between fluoride and the pineal gland’s function remains an area of ongoing research. While fluoride’s benefits for dental health are well-documented, its potential effects on the endocrine system, particularly melatonin production, warrant further investigation. By balancing fluoride intake and staying informed, individuals can make choices that support both dental and overall health.
References
【1】"The Pineal Gland and Melatonin Production: Impacts of Fluoride," Applied Sciences, MDPI. Available at: https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3417/10/8/2885
【2】"Pineal Calcification and Its Impact on Melatonin Synthesis," Molecules, PMC. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6017004
【3】"Fluoride Exposure and Sleep Patterns in Adolescents," Environmental Health, BioMed Central. Available at: https://ehjournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12940-019-0546-7
【4】"Decalcifying the Pineal Gland: Myths and Facts," Healthline. Available at: https://www.healthline.com/health/decalcify-pineal-gland
Other Articles

LY 53A Vital-G Body Maintenance Cream (w...
Unlock the secret to long-term vitality and holistic body wellness. Combining natural ingredients wi...

How LY Vital-G Body Maintenance Cream Su...
The LY Vital-G Body Maintenance Cream, formulated with Glucosamine and MSM, is designed to promote j...
Pre-Exercise Lubrication and Post-Exerci...
Maintaining optimal muscle and joint health is essential for anyone engaging in physical activity, w...

LY 12A RevitaPūr Face Wash
It is imperative to choose a facial wash that suits your skin type and lifestyle. Using the right fa...
